fadi

FADI - Ingest, store and analyse big data flows
Use Case - Streaming ingestion with Apache Kafka
This page provides documentation on how to use the FADI big data framework using a sample use case: monitoring CETIC offices building.
- 1. Install FADI
- 2. Prepare the database to store measurements
- 3. Ingest and Digest measurements
- 4. Display dashboards and configure alerts
- 5. Explore
- 6. Process
- 7. Summary
In this example, we will ingest temperature measurements from sensors and push them into the Apache Kafka message broker. We are then going to store the data from the broker into a database. Finally, we display the temperature values in a simple dashboard.
1. Install FADI
To install the FADI framework on your workstation or on a cloud, see the installation instructions.
The components needed for this use case are the following:
- Apache Nifi as a integration tool to ingest the sensor data from the data source (a csv file in this case) and push it into the broker. We also use Apache Nifi to get the data back from the broker ans store it into the database.
- Apache Kafka as a message broker.
- PostgreSQL as both a datawarehouse and datalake
- Gafana as a dashboard tool to display graphs from the data ingested and stored in the datalake
- Superset as a exploration dashboard tool
- Jupyter as a web interface to explore the data using notebooks
Those components are configured in the following sample config file.
The following instructions assume that you deployed FADI on your workstation inside minikube.
Unless specified otherwise, all services can be accessed using the username and password pair: admin / password1 , see the user management documentation for detailed information on how to configure user identification and authorization (LDAP, RBAC, …).
2. Prepare the database to store measurements
First, setup the datalake by creating a table in the postgresql database.
To achieve this you need to:
- Head to the adminer interface, if you are using minikube, you can use the following command :
minikube service -n fadi fadi-adminer -
Access to the adminer service and to the postgreSQL database using the following credentials:
- System: PostgreSQL
- Server: fadi-postgresql
- Username: admin
- Password: passowrd1
- Database: postgres
-
In the adminer Browser, launch the Query tool by clicking “SQL command”.
-
Copy/Paste the table creation script in the Query Editor.
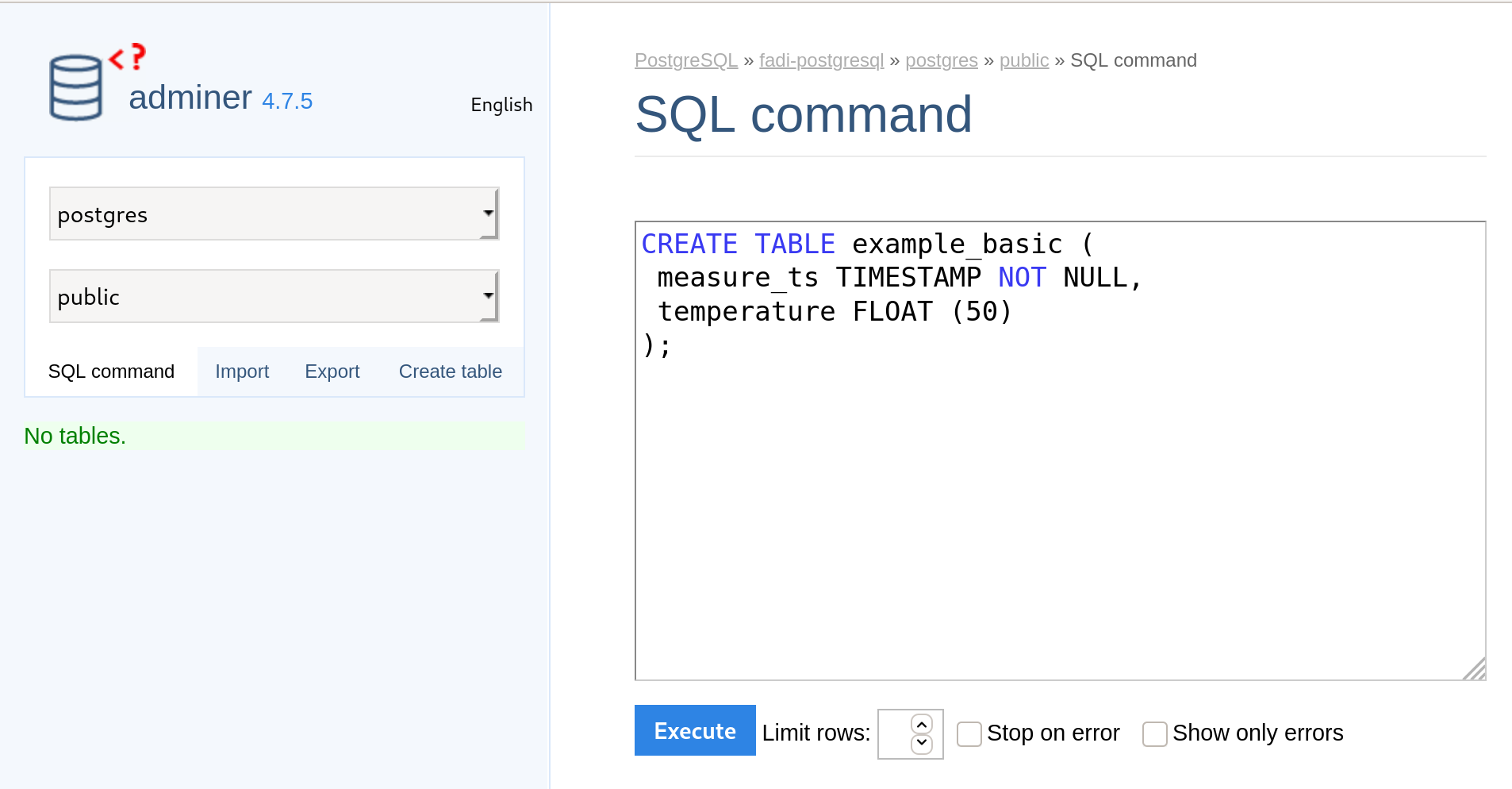
-
Execute the creation query by clicking on the
Executecommand. - Once the previous steps are finished, you can detect that a new table
example_basicis created in theTablesfield of adminer Browser.
3 Prepare Nifi to inter-connect the different components.
“An easy to use, powerful, and reliable system to process and distribute data.”
Apache Nifi provides data ingestion and processing mechanism (to e.g. connect a database, REST API, csv/json/avro files on a FTP, …): in this case we want to read the temperature sensors data from our HVAC system and store it in a database while using a broker to transmit the data between the various processing steps.
To start, head to the Nifi web interface, if you are using minikube, you can use the following command :
minikube service -n fadi fadi-nifi
For more information on how to use Apache Nifi, see the official Nifi user guide and this Awesome Nifi resources.
3.1 Measurements ingestion
Temperature measurements from the last 5 days (see HVAC sample temperatures csv extract) are ingested:
measure_ts,temperature
2019-06-23 14:05:03.503,22.5
2019-06-23 14:05:33.504,22.5
2019-06-23 14:06:03.504,22.5
2019-06-23 14:06:33.504,22.5
2019-06-23 14:07:03.504,22.5
2019-06-23 14:07:33.503,22.5
2019-06-23 14:08:03.504,22.5
2019-06-23 14:08:33.504,22.5
(...)
Now we need to tell Nifi to read the csv file and push the measurements in broker, this can be done by creating the following components in Nifi:
Processors
To create processor, make a drag and drop from the following button :

We need to configure two processors:
- InvokeHTTP processor:
- right-click on the processor > Click on
Configure>- On the
Settingstab >Automatically Terminate Relationships: all exceptResponse - On the
Propertiestab >Remote url:https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cetic/fadi/master/examples/kafka/sample_data.csv - On the
Schedulingtab >Run Schedule: 120s (this will download the sample file every 120 seconds)
- On the
- right-click on the processor > Click on
- PublishKafka processor:
- right-click on the processor > Click on
Configure> go toPropertiestab >Kafka Brokers:fadi-kafka:9092Topic Name:nifi-kafka
- right-click on the processor > Click on
Output Port
To create output port, make a drag and drop from the following button :

Create two output ports : success_port and failure_port
Connections
ResponseConnection:- Create an edge from
InvokeHTTPprocessor toPublishKafka - Details > For relationships >
Response
- Create an edge from
SuccessConnection:- Create an edge from
PutDatabaseRecordtoOutput Success Port - Details > relationships > only
success
- Create an edge from
FailureConnection:- From
PutDatabaseRecordtoOutput Failure Port - Details > relationships > : only
failure
- From
Here is the target result :
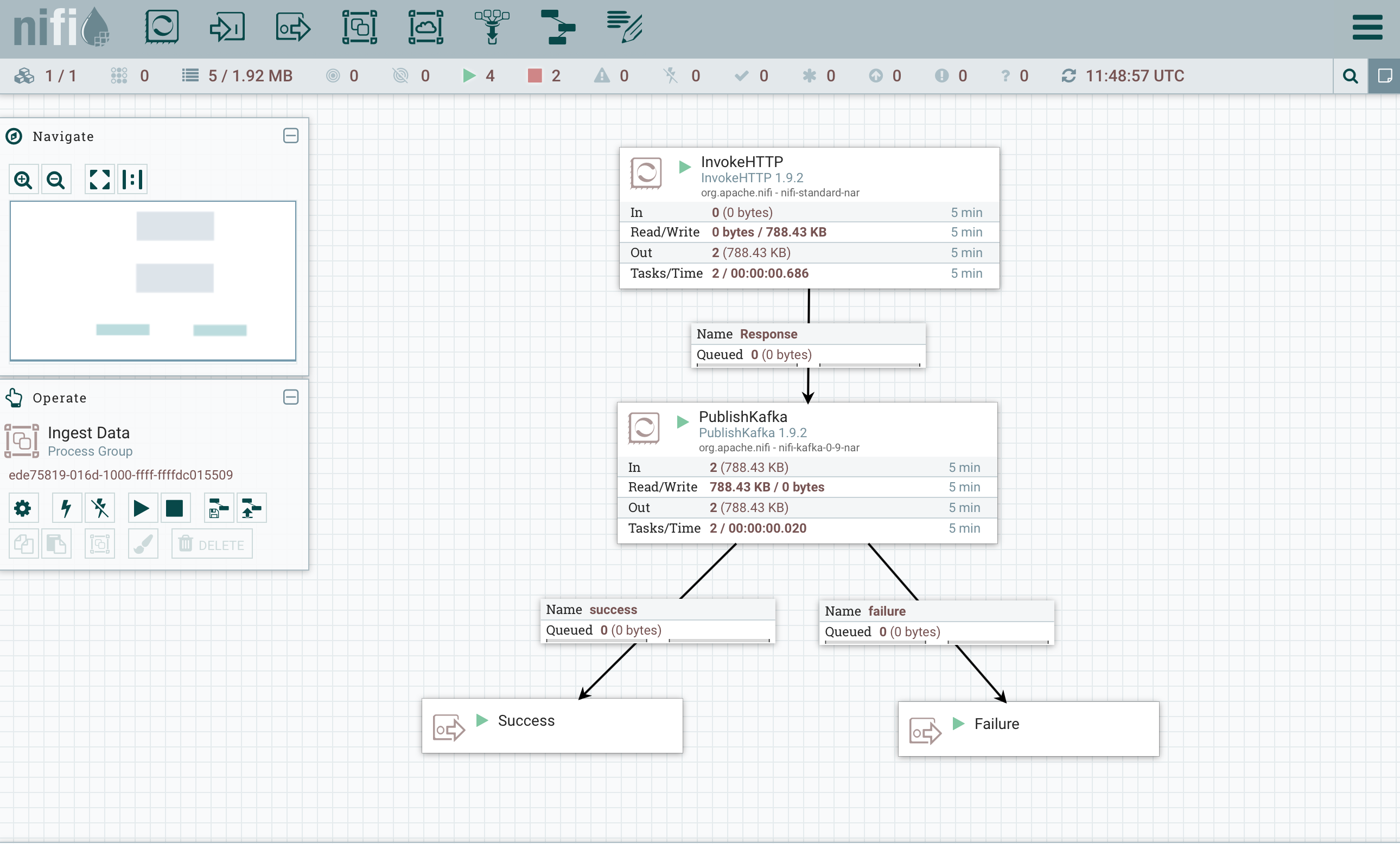
See also the Nifi “Kafka_to_PostgreSQL” template that corresponds to this example.
To reuse the provided template (instead of designing your own template), you can:
- Click
Upload templatein the Operate frame, select the template, and upload it. - From the Nifi menu, drag and drop the Template menu.
- Choose your uploaded template.
- right-click, and select
Start.
3.2 Measurements digestion
Processors
To create the processor, drag and drop from the following button :

We need to configure two processors:
ConsumeKafkaprocessor- right-click on the processor > Click on
Configure> go toPropertiestab >Kafka Brokers:fadi-kafka:9092Topic Name:nifi-kafkaGroup ID:fadiOffset Reset:earliest
- right-click on the processor > Click on
PutDatabaseRecordprocessor:- right-click on the processor > Click on
Configure> go toSettingstab > uncheck all the box on the listAutomatically Terminate Relationships - right-click on the processor > Click on
Configure> go toPropertiestab >
- Statement Type:
INSERT - Schema Name >
public - Table Name >
example_basic - Translate Field Names >
false* right-click on the processor > Click onConfigure> go toPropertiestab > Record Reader >Create a new service>CSV Reader> click onGo To(the litlle arrow on the right) > Click onConfigure(the gear on the right side) >Properties> setTreat First Line as Headertotrue* right-click on the processor > Click onConfigure> go toPropertiestab > Database Connection Pooling Service >DBCPConnectionPool> Click onGo To(the litlle arrow on the right) > Click onConfigure(the gear on the right side) >Properties> set up the following values: - Database Connection URL:
jdbc:postgresql://fadi-postgresql:5432/postgres?stringtype=unspecified - Database Driver Class Name:
org.postgresql.Driver - Database Driver Location(s):
/opt/nifi/psql/postgresql-42.2.6.jar - Database User:
admin - Password:
password1 - Enable service by clicking on the lightning icon.
- right-click on the processor > Click on
Output Port
To create output port, make a drag and drop from the following button :

Create two output ports : success_port and failure_port
Connections
ResponseConnection:- Create an edge from
InvokeHTTPprocessor toPublishKafka - Details > For relationships >
Response
- Create an edge from
SuccessConnection:- Create an edge from
PutDatabaseRecordtoOutput Success Port - Details > relationships > only
success
- Create an edge from
FailureConnection:- From
PutDatabaseRecordtoOutput Failure Port - Details > relationships > : only
failure
- From
Here is the result you need to arrive to:
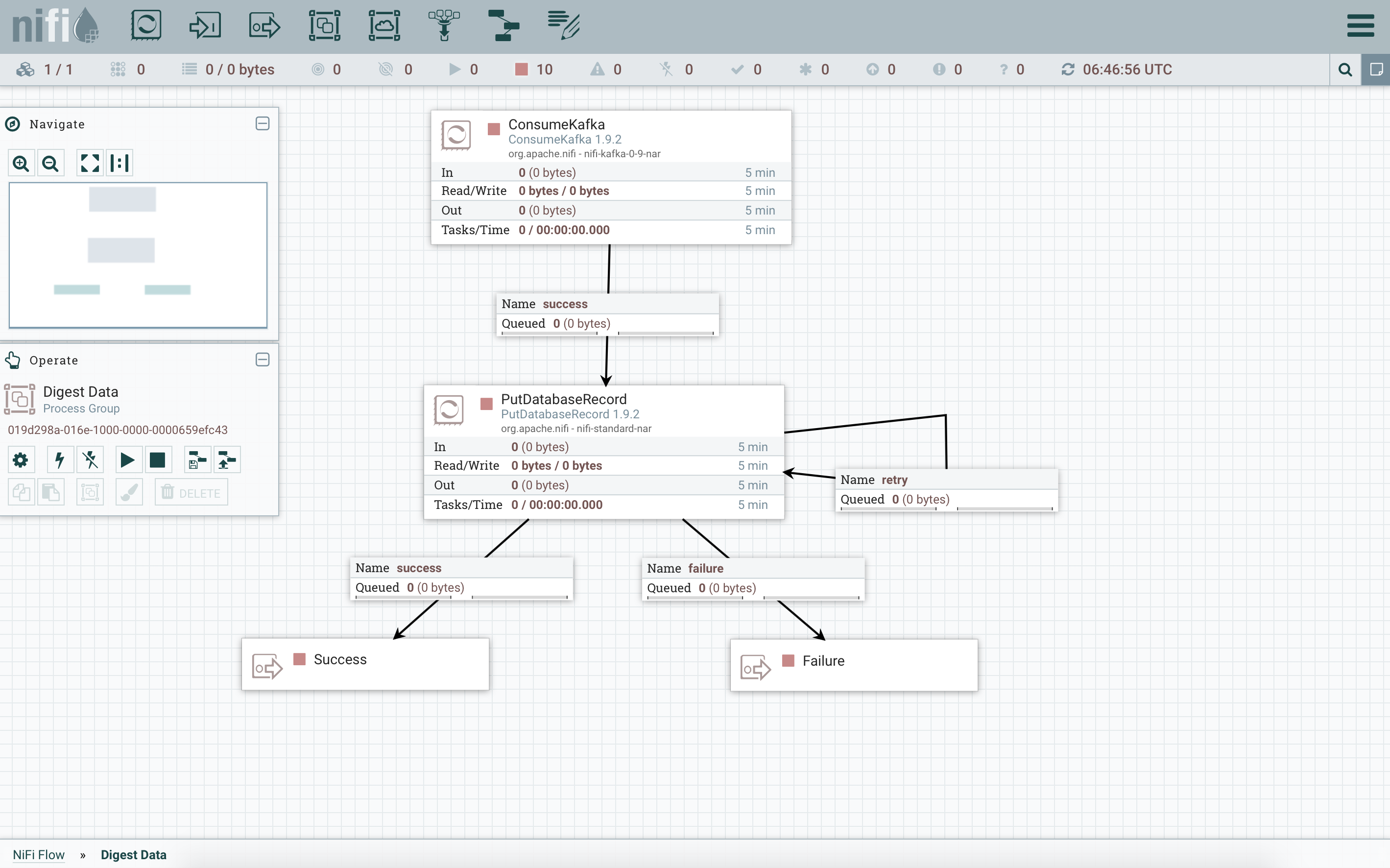
See also the Nifi “CSV_to_Kafka” template that corresponds to this example.
To reuse the provided template (instead of designing your own template), you can:
- Click
Upload templatein the Operate frame, select the template, and upload it. - From the Nifi menu, drag and drop the Template menu.
- Choose your uploaded template.
- In the Operate frame of Nifi:
- right-click on
Configuration - Click on
View configurationofDBCPConnectionPoolcontroller service. - In the
Propertiestab, complete thepasswordfield withpassword1 - Enable both
CSVReaderandDBCPConnectionPoolcontroller services. - right-click, and select
Start.
- right-click on
For more information on how to use Apache Nifi, see the official Nifi user guide and this Awesome Nifi resources.
Finally, start the Nifi flow in the operate window.
4. Display dashboards and configure alerts
This step is similar to the basic use case
5. Explore
This step is similar to the basic use case
6. Process
This step is similar to the basic use case
7. Summary
In this use case, we have demonstrated a streaming configuration for FADI, where we use various services to ingest, store, analyse, explore and provide dashboards and alerts.


