fadi

FADI - Ingest, store and analyse big data flows
TSimulus: Sensors simulation for FADI
0. Context
The TSimulus library is used to simulate various sensors from industrial partners in the context of many research projects. It allows to generate a sufficient amount of data to test the entire FADI platform. It is useful when there was a lack of real time data streams. In that context, TSimulus enables to already work on the analysis part without having the real data from the partners.
This section explains how to setup TSimulus for FADI and gives the essential links to the documentation on how to use it.
1. Setup TSimulus
The TSimulus as a Service project aims at building a REST API in front of the TSimulus framework, and a set of configurable websocket routes to consume the TSimulus stream.
The project is structured as a sbt multiproject, each part is runnable as standalone and the top level project orchestrates a complete deployment and coordination of each parts.
For more information on the implementation, take a look at the documentation of TSimulus as a Service.
To install TSimulus with FADI, you will need to modify a bit the values.yaml file. This will deploy all the TSimulus services (the TSimulus microservice and the Swagger User Interface) on your Kubernetes cluster.
First of all, update your values.yaml by activating the TSimulus services:
tsaas:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: true
hosts: [api-tsimulus.yourdomain]
swaggerui:
enabled: true
swaggerui :
jsonUrl : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cetic/tsimulus-saas/master/oas/api-doc/openapi.json
server :
url: http://api-tsimulus.yourdomain
description: "TSIMULUS API"
ingress:
enabled: true
hosts: [swagger-tsimulus.yourdomain]
You can also setup Ingress parts to use a reverse proxy. See the previous section.
Then, run the deploy.sh script to take the modifications into account:
cd helm
./deploy.sh
You should now be able to access the Swagger User Interface (on a minikube setup: minikube service fadi-swaggerui):
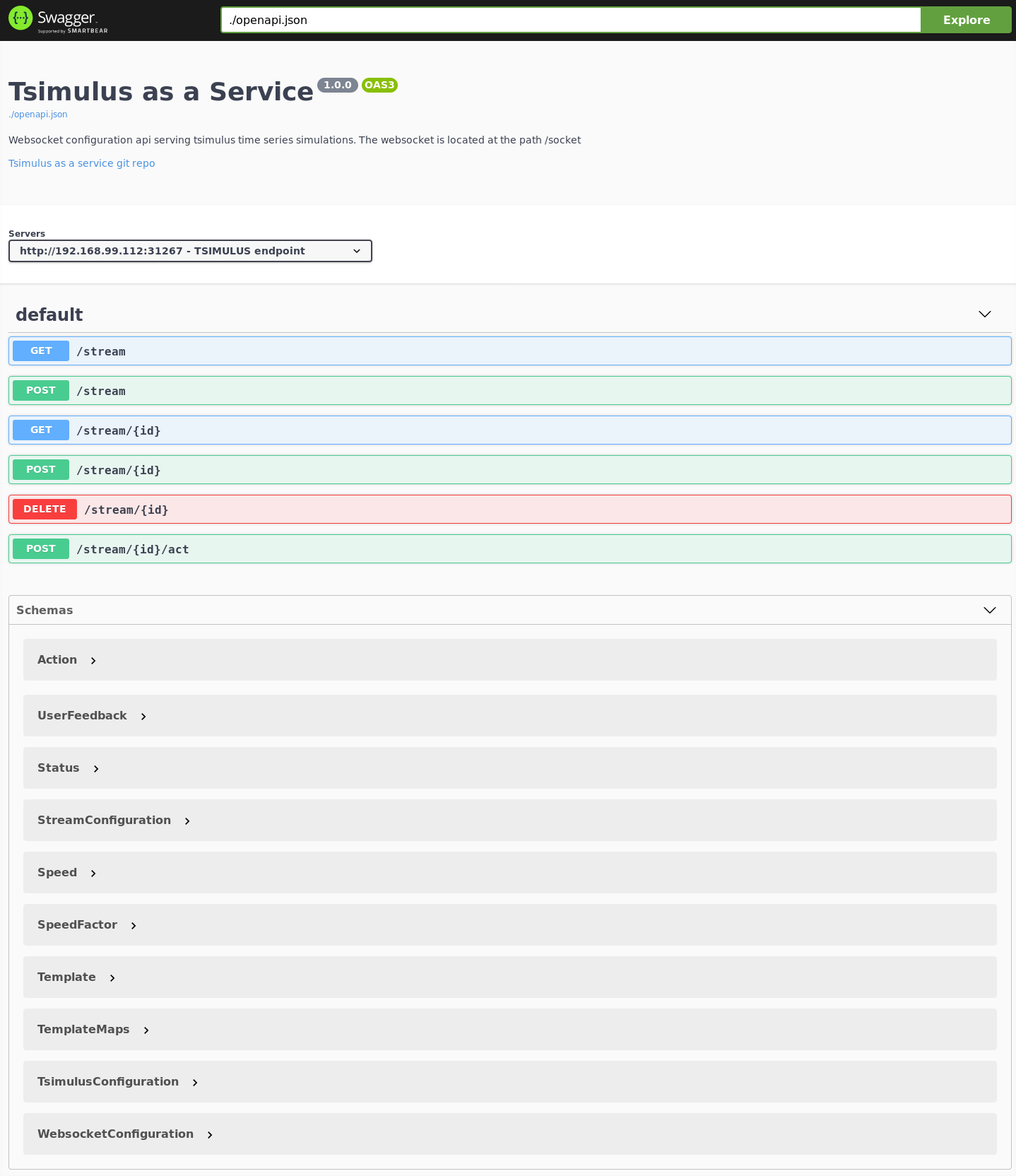
2. How to use TSimulus?
- See the TSimulus Documentation.
- See the TSimulus as a Service Documentation.
- (TODO) See the use cases.
